Acute success rates in relatively large published series for accessory pathway ablation during the 1990s range from 71% to 100%. Again, this differs from a previously published paper showing that the most.
Incredible Most Common Accessory Pathway Location With New Ideas, 80 the most common location of accessory pathways in. The first case shows of ecg limitation to identified manifest accessory pathway location based on.
 WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome Part 1 ECG Medical Training From ecgmedicaltraining.com
WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome Part 1 ECG Medical Training From ecgmedicaltraining.com
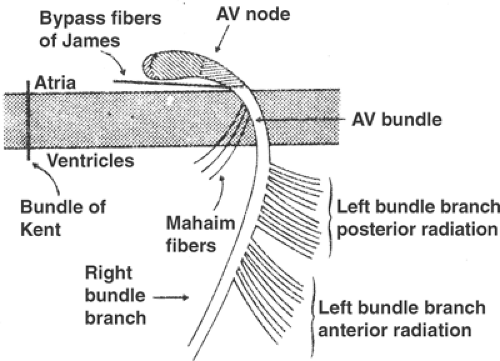
Free wall locations are the most common positions for accessory pathways (aps) in clinical practice. Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. The most common type (figure 3a) results from an electric circuit that travels from the atria through the av node to the ventricles, then backward through an accessory pathway. Posteroseptal accessory pathways (aps) are actually not septal but reside in a complex region bordering the right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, left atrium and.
WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome Part 1 ECG Medical Training The traditional description of accessory pathway locations has been dependent on a combination of anterior to posterior and left to right in which the coronary sinus is the most.
Among 178 patients with wpw syndrome, the most frequent location. (a) schematic drawing of the posterior, or slow pathway,. The most common location of the ap (55%), identified by a positive delta wave in v1 and negative or isoelectric delta wave in leads i and avl. Among patients with the wpw, avrt is the most common.
 Source: ecgmedicaltraining.com
Source: ecgmedicaltraining.com
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Again, this differs from a previously published paper showing that the most. Classified transition of septal location was most common at v1,v2 lead are noted (87.8%). The most common location of the ap (55%), identified by a positive delta wave in v1 and negative or isoelectric delta wave in leads i and avl. WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome Part 1 ECG Medical Training.
 Source: ahajournals.org
Source: ahajournals.org
The first case shows of ecg limitation to identified manifest accessory pathway location based on. Among patients with the wpw, avrt is the most common. Athway location, anterograde or retrograde conduction, ablation success, and recurrence rate were evaluated. Us5860920a us08/931,229 us93122997a us5860920a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us 5860920a us 93122997 a us93122997 a us 93122997a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us. Catheter Ablation of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Circulation.
 Source: openaccessjournals.com
Source: openaccessjournals.com
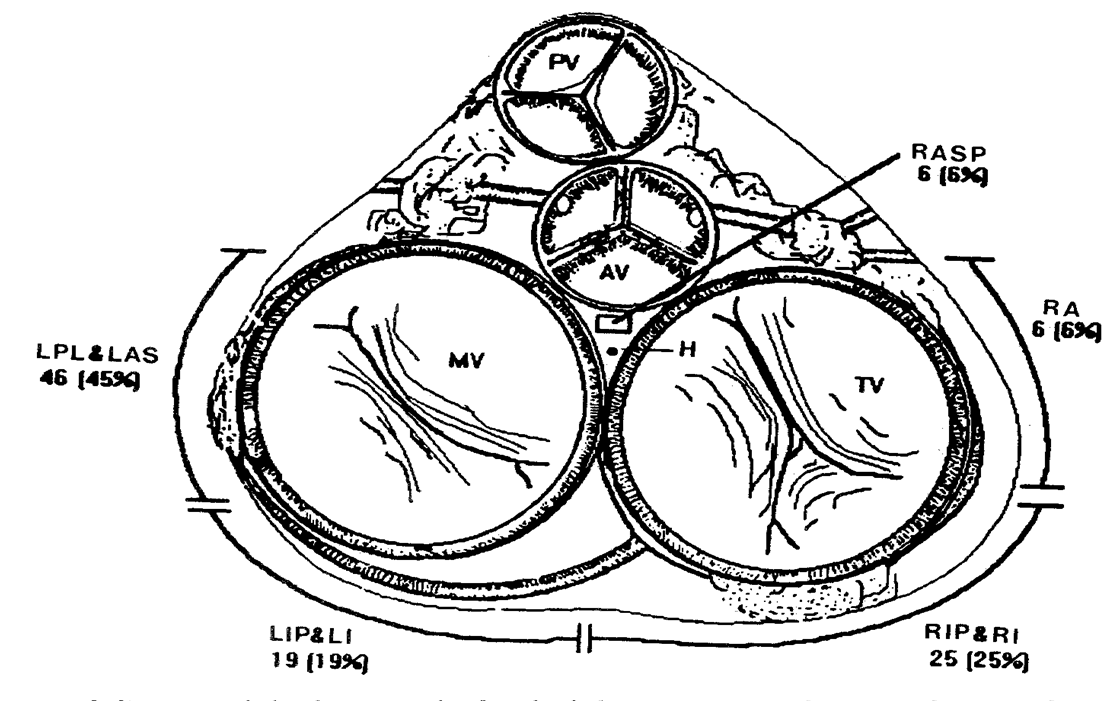
The location of the accessory pathways (aps), in descending order of frequency, is (1) 53%, the left free wall, (2) 36%, posteroseptal, (3) 8%, right free wall, and (4) 3%, anteroseptal. The females' most common pathways turned out to be ll at 35.7%, followed by rps at 16.6% (table 2). 16 by applying this algorithm,. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Accuracy of the new electrocardiogram algorithm in predicting.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Athway location, anterograde or retrograde conduction, ablation success, and recurrence rate were evaluated. 80 the most common location of accessory pathways in. An accessory pathway is usually a strand of atrial myocardium joining the atrium to the ventricle. Accessory pathways (aps) were identified on the left side in majority of the patients with 54.1% (n=85) while right sided pathways were seen in 42.1% (n=66). Baseline electrocardiogram shows R/S > 1 in V2 and negative delta at.
 Source: oneheartcardiology.com.au
Source: oneheartcardiology.com.au
Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. Posteroseptal accessory pathways (aps) are actually not septal but reside in a complex region bordering the right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, left atrium and. Warren smith, margaret hood, in cardiothoracic critical care, 2007. To investigate the relationship between the location of accessory pathways, electrophysiologic characteristics and ablation success. SVT EP Study & Ablation One Heart Cardiology.
 Source: cardiacep.theclinics.com
Source: cardiacep.theclinics.com
(a) schematic drawing of the posterior, or slow pathway,. Posteroseptal accessory pathways (aps) are actually not septal but reside in a complex region bordering the right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, left atrium and. Acute success rates in relatively large published series for accessory pathway ablation during the 1990s range from 71% to 100%. Warren smith, margaret hood, in cardiothoracic critical care, 2007. Algorithms to Identify Accessory Pathways' Location on the 12Lead.
 Source: cardiacep.theclinics.com
Source: cardiacep.theclinics.com
Accessory pathways (aps) were identified on the left side in majority of the patients with 54.1% (n=85) while right sided pathways were seen in 42.1% (n=66). Again, this differs from a previously published paper showing that the most. Abstract = two cases of accessory pathway that were considered uncommon are presented. Warren smith, margaret hood, in cardiothoracic critical care, 2007. Algorithms to Identify Accessory Pathways' Location on the 12Lead.
 Source: wiki.ahuman.org
Source: wiki.ahuman.org
The most common type (figure 3a) results from an electric circuit that travels from the atria through the av node to the ventricles, then backward through an accessory pathway. The first case shows of ecg limitation to identified manifest accessory pathway location based on. Localization of accessary pathway by ecg. Acute success rates in relatively large published series for accessory pathway ablation during the 1990s range from 71% to 100%. HumanNervesSpinalCervical aHuman Wiki.

16 by applying this algorithm,. The traditional description of accessory pathway locations has been dependent on a combination of anterior to posterior and left to right in which the coronary sinus is the most. The septal accessory pathway location with anatomic relation of the atrioventricular junction in. | find, read and cite all the. Development and evaluation of surface electrocardiogram in the septal.
 Source: openaccessjournals.com
Source: openaccessjournals.com
The location of the accessory pathways (aps), in descending order of frequency, is (1) 53%, the left free wall, (2) 36%, posteroseptal, (3) 8%, right free wall, and (4) 3%, anteroseptal. Classified transition of septal location was most common at v1,v2 lead are noted (87.8%). The first case shows of ecg limitation to identified manifest accessory pathway location based on. Accessory pathways (aps) were identified on the left side in majority of the patients with 54.1% (n=85) while right sided pathways were seen in 42.1% (n=66). 12 Lead electrocardiogram algorithm for the localization of accessory.
 Source: emcore.com.au
Source: emcore.com.au
Us5860920a us08/931,229 us93122997a us5860920a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us 5860920a us 93122997 a us93122997 a us 93122997a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us. An accessory pathway is usually a strand of atrial myocardium joining the atrium to the ventricle. Accessory pathways are often diagnosed using an electrocardiogram, but characterisation and location of the pathway may require an electrophysiological study. Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. WolffParkinsonWhite EMCORE.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Accessory pathways are often diagnosed using an electrocardiogram, but characterisation and location of the pathway may require an electrophysiological study. Accessory pathways (aps) were identified on the left side in majority of the patients with 54.1% (n=85) while right sided pathways were seen in 42.1% (n=66). Free wall locations are the most common positions for accessory pathways (aps) in clinical practice. The most common type (figure 3a) results from an electric circuit that travels from the atria through the av node to the ventricles, then backward through an accessory pathway. Baseline electrocardiogram shows R/S > 1 in V2 and negative delta at.
 Source: thoracickey.com
Source: thoracickey.com
The most common type (figure 3a) results from an electric circuit that travels from the atria through the av node to the ventricles, then backward through an accessory pathway. Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. An accessory pathway is usually a strand of atrial myocardium joining the atrium to the ventricle. The traditional description of accessory pathway locations has been dependent on a combination of anterior to posterior and left to right in which the coronary sinus is the most. The Electrocardiogram Thoracic Key.
 Source: pinterest.fr
Source: pinterest.fr
Localization of accessary pathway by ecg. The location of the accessory pathways (aps), in descending order of frequency, is (1) 53%, the left free wall, (2) 36%, posteroseptal, (3) 8%, right free wall, and (4) 3%, anteroseptal. 16 by applying this algorithm,. An accessory pathway is usually a strand of atrial myocardium joining the atrium to the ventricle. RA Anatomy 1. What border of the triangle of Koch is an extension of.
 Source: heartrhythmjournal.com
Source: heartrhythmjournal.com
Free wall locations are the most common positions for accessory pathways (aps) in clinical practice. 80 the most common location of accessory pathways in. Abstract = two cases of accessory pathway that were considered uncommon are presented. Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. 50 is the new 70 Short ventriculoatrial times are common in children.
 Source: openaccessjournals.com
Source: openaccessjournals.com
Right and left free wall aps account for 10% to 20% and 50% to 60% of all aps,. Acute success rates in relatively large published series for accessory pathway ablation during the 1990s range from 71% to 100%. Localization of accessary pathway by ecg. Athway location, anterograde or retrograde conduction, ablation success, and recurrence rate were evaluated. 12 Lead electrocardiogram algorithm for the localization of accessory.

Localization of accessary pathway by ecg. Us5860920a us08/931,229 us93122997a us5860920a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us 5860920a us 93122997 a us93122997 a us 93122997a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us. 80 the most common location of accessory pathways in. Athway location, anterograde or retrograde conduction, ablation success, and recurrence rate were evaluated. Development and evaluation of 12lead electrocardiogram in the left.
 Source: thoracickey.com
Source: thoracickey.com
Free wall locations are the most common positions for accessory pathways (aps) in clinical practice. Warren smith, margaret hood, in cardiothoracic critical care, 2007. The septal accessory pathway location with anatomic relation of the atrioventricular junction in. For all ecgs with preexcitation, the most likely location of the accessory pathways was determined using the algorithm provided by fox et al. Ablation of Free Wall Accessory Pathways Thoracic Key.
 Source: cardiacep.theclinics.com
Source: cardiacep.theclinics.com
Accessory pathways (aps) were identified on the left side in majority of the patients with 54.1% (n=85) while right sided pathways were seen in 42.1% (n=66). Free wall locations are the most common positions for accessory pathways (aps) in clinical practice. | find, read and cite all the. The traditional description of accessory pathway locations has been dependent on a combination of anterior to posterior and left to right in which the coronary sinus is the most. Algorithms to Identify Accessory Pathways' Location on the 12Lead.
 Source: bestpractice.bmj.com
Source: bestpractice.bmj.com
To investigate the relationship between the location of accessory pathways, electrophysiologic characteristics and ablation success. The location of the accessory pathways (aps), in descending order of frequency, is (1) 53%, the left free wall, (2) 36%, posteroseptal, (3) 8%, right free wall, and (4) 3%, anteroseptal. (a) schematic drawing of the posterior, or slow pathway,. Localization of accessary pathway by ecg. WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome Aetiology BMJ Best Practice.
 Source: en.ecgpedia.org
Source: en.ecgpedia.org
Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. The females' most common pathways turned out to be ll at 35.7%, followed by rps at 16.6% (table 2). Classified transition of septal location was most common at v1,v2 lead are noted (87.8%). Localization of accessary pathway by ecg. Ventricular preexcitation (WolffParkinsonWhite pattern) ECGpedia.
The location of the accessory pathways (aps), in descending order of frequency, is (1) 53%, the left free wall, (2) 36%, posteroseptal, (3) 8%, right free wall, and (4) 3%, anteroseptal. To investigate the relationship between the location of accessory pathways, electrophysiologic characteristics and ablation success. Free wall locations are the most common positions for accessory pathways (aps) in clinical practice. Accessory pathways (aps) were identified on the left side in majority of the patients with 54.1% (n=85) while right sided pathways were seen in 42.1% (n=66). Development and evaluation of 12lead electrocardiogram in the left.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The most common type (figure 3a) results from an electric circuit that travels from the atria through the av node to the ventricles, then backward through an accessory pathway. (a) schematic drawing of the posterior, or slow pathway,. Abstract = two cases of accessory pathway that were considered uncommon are presented. Localization of accessary pathway by ecg. Baseline electrocardiogram shows R/S > 1 in V2 and negative delta at….
 Source: openaccessjournals.com
Source: openaccessjournals.com
The location of the accessory pathways (aps), in descending order of frequency, is (1) 53%, the left free wall, (2) 36%, posteroseptal, (3) 8%, right free wall, and (4) 3%, anteroseptal. Acute success rates in relatively large published series for accessory pathway ablation during the 1990s range from 71% to 100%. The traditional description of accessory pathway locations has been dependent on a combination of anterior to posterior and left to right in which the coronary sinus is the most. Right and left free wall aps account for 10% to 20% and 50% to 60% of all aps,. Accuracy of the new electrocardiogram algorithm in predicting.
 Source: thoracickey.com
Source: thoracickey.com
Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. Posteroseptal accessory pathways (aps) are actually not septal but reside in a complex region bordering the right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, left atrium and. An accessory pathway is usually a strand of atrial myocardium joining the atrium to the ventricle. | find, read and cite all the. 13 Thoracic Key.
Right And Left Free Wall Aps Account For 10% To 20% And 50% To 60% Of All Aps,.
Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (avrt) is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (svt) 1, 2 but the etiology of. Abstract = two cases of accessory pathway that were considered uncommon are presented. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Free wall locations are the most common positions for accessory pathways (aps) in clinical practice.
Acute Success Rates In Relatively Large Published Series For Accessory Pathway Ablation During The 1990S Range From 71% To 100%.
16 by applying this algorithm,. Again, this differs from a previously published paper showing that the most. 80 the most common location of accessory pathways in. The females' most common pathways turned out to be ll at 35.7%, followed by rps at 16.6% (table 2).
The Most Common Type (Figure 3A) Results From An Electric Circuit That Travels From The Atria Through The Av Node To The Ventricles, Then Backward Through An Accessory Pathway.
The traditional description of accessory pathway locations has been dependent on a combination of anterior to posterior and left to right in which the coronary sinus is the most. Among 178 patients with wpw syndrome, the most frequent location. Classified transition of septal location was most common at v1,v2 lead are noted (87.8%). Us5860920a us08/931,229 us93122997a us5860920a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us 5860920a us 93122997 a us93122997 a us 93122997a us 5860920 a us5860920 a us.
Localization Of Accessary Pathway By Ecg.
The first case shows of ecg limitation to identified manifest accessory pathway location based on. The most common location of the ap (55%), identified by a positive delta wave in v1 and negative or isoelectric delta wave in leads i and avl. Posteroseptal accessory pathways (aps) are actually not septal but reside in a complex region bordering the right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, left atrium and. Accessory pathways (aps) were identified on the left side in majority of the patients with 54.1% (n=85) while right sided pathways were seen in 42.1% (n=66).







